How to Perfect Your Kettlebell Deadlift
The kettlebell deadlift is a fundamental strength training exercise that builds powerful glutes, hamstrings, and core stability while reinforcing safe lifting mechanics. Unlike barbell deadlifts, the kettlebell version is easier to learn, making it an excellent choice for beginners and advanced athletes alike. Mastering this movement will improve your posture, functional strength, and overall athletic performance.
Instructions
Setup
-
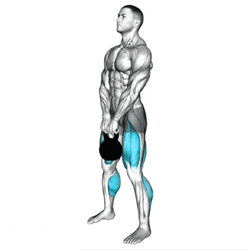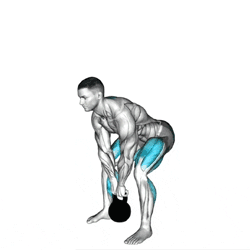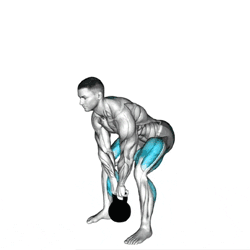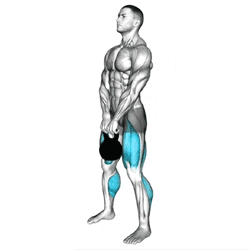
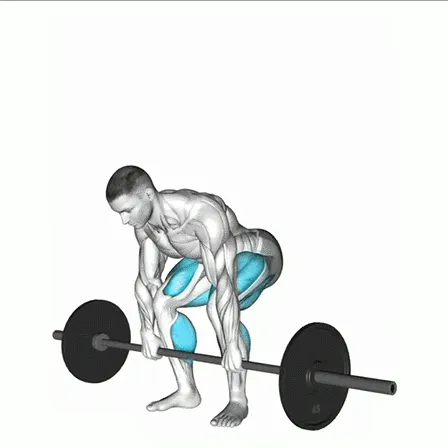
Foot Position: Stand with your feet about hip-width apart. Place the kettlebell directly between your feet, handle aligned with your midfoot.
-
Grip: Reach down and grab the handle with both hands, palms facing you or slightly inward. Keep your grip firm.
-
Posture: Engage your core, pull your shoulders back, and maintain a neutral spine. Avoid rounding or over-arching your back.
-
Hinge at the Hips: Push your hips back instead of bending your knees too much. Keep your shins vertical or only slightly forward.
Lift Off (The Pull)
-
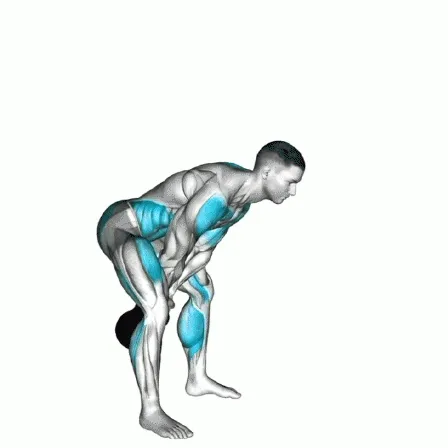
Initiate the Lift: Drive your hips forward and stand tall while pulling the kettlebell upward. Focus on glutes and hamstrings, not arms.
-
Core Engagement: Keep your core braced to protect your lower back. Your chest and hips should rise together.
-
Stand Tall: At the top, extend your hips fully, keeping your shoulders back and chest lifted. Avoid leaning back.
Lowering the Kettlebell
-
Hip Hinge: Push your hips back first as you lower the kettlebell, maintaining a neutral spine.
-
Kettlebell Path: Keep the kettlebell close to your body, lowering it along the same vertical path as the lift.
-
Knees and Hips: Once the kettlebell passes your knees, bend them slightly and return the weight to the floor with control.
Tips for Proper Form
-
Speed & Efficiency: In high-rep workouts (like CrossFit), move briskly while maintaining good form. Don’t let fatigue compromise your technique.
-
Breathing: Inhale before lifting to brace your core, and exhale at the top. Avoid holding your breath for too long.
-
Use Proper Weight: Start light to master form before progressing to heavier kettlebells.
-
Hip Mobility: Work on hip and hamstring flexibility to improve your hinge movement.
-
Progression: Begin with bodyweight or a light kettlebell before moving to heavier loads.
-
Scaling Options: Use a dumbbell, barbell, or elevated kettlebell (box deadlift) if you’re still learning the movement.
Benefits of Kettlebell Deadlifts
-
Builds lower-body strength, targeting glutes, hamstrings, and quads.
-
Improves core stability and posture by reinforcing proper bracing mechanics.
-
Enhances hip hinge movement, which is essential for safe lifting and athletic performance.
-
Reduces injury risk by teaching correct lifting form for everyday activities.
-
Versatile training tool, great for strength training, CrossFit, or conditioning workouts.
-
Beginner-friendly alternative to the barbell deadlift, with easier setup and safer progression.
The kettlebell deadlift is a simple yet powerful exercise that develops strength, stability, and functional movement patterns. By focusing on hip hinge mechanics and proper posture, you can safely increase your strength and carryover to other lifts. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced lifter, this exercise is a must-have in your training program.