Kettlebell Swings: Proper Form, Benefits, and Step-by-Step Guide for Strength & Fat Loss
Kettlebell swings are one of the most effective exercises for building explosive power, strength, and endurance. This dynamic movement targets the entire posterior chain while also improving cardiovascular fitness, grip strength, and core stability.
Instructions
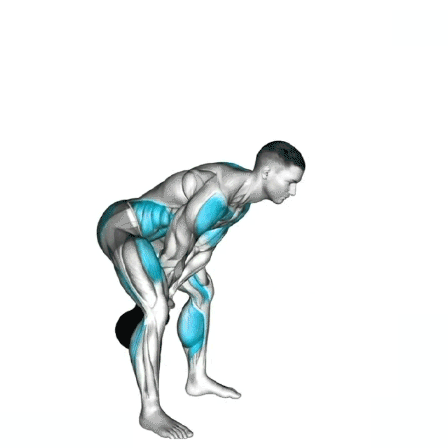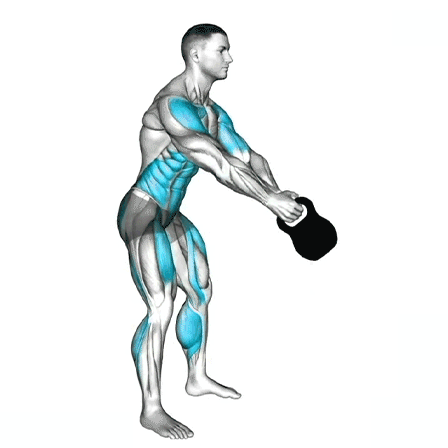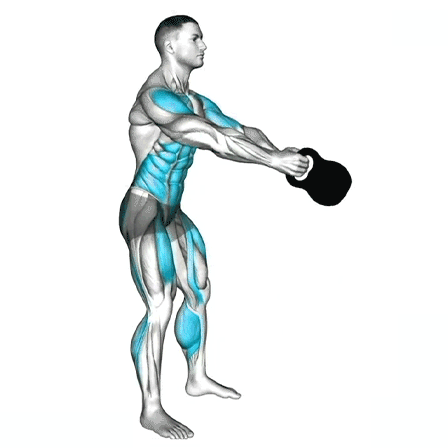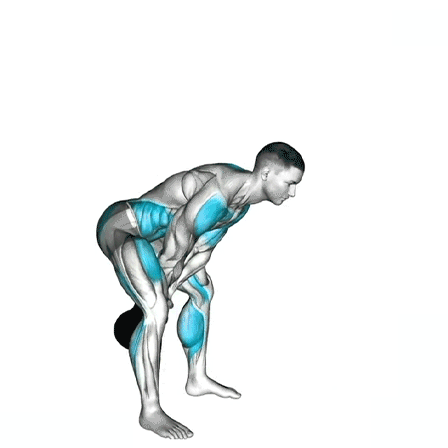
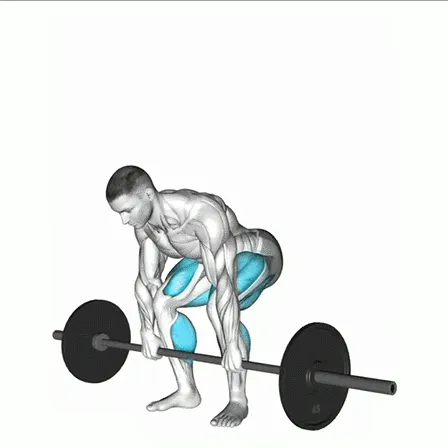
1. Starting Position
-
Feet: Place feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, toes angled slightly outward.
-
Grip: Hold the kettlebell handle with both hands, arms extended in front of you, palms facing the body. Wrap your thumbs securely around the handle.
-
Posture: Keep your chest lifted, back neutral, and shoulders pulled down. Maintain a slight bend in your knees.
2. Hinge and Load
-
Hip Hinge: Push your hips back (not down like a squat), allowing the kettlebell to swing between your legs.
-
Core Engagement: Brace your abs to protect your lower back and maintain a neutral spine.
-
Loading: Let the kettlebell drop just past your knees or to mid-shin height.
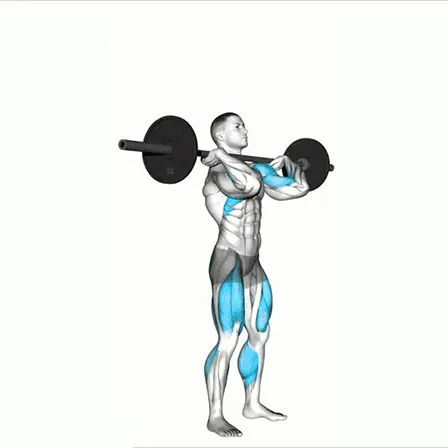
3. The Swing
-
Hip Drive: Explosively thrust your hips forward, using glutes and hamstrings to power the movement.
-
Height: The kettlebell should rise to shoulder height for a Russian swing, or overhead for an American swing (only if your core is strong and stable).
-
Arms: Keep arms relaxed; they should guide the kettlebell, not lift it.
4. The Descent
-
Controlled Drop: Guide the kettlebell down with a hip hinge, not a squat.
-
Repeat: Once the kettlebell reaches the bottom, thrust your hips again to continue the swing.
Tips
-
Engage Glutes: Squeeze glutes at the top of each swing to maximize power and protect your back.
-
Neutral Spine: Avoid rounding your back or overextending your neck.
-
Hip-Powered: The movement comes from the hips, not the arms.
-
Breathing: Exhale forcefully on the hip thrust, inhale on the downswing.
-
Don’t Squat: Keep knees soft but hinge from the hips instead of squatting.
-
Kettlebell Height: Stick to shoulder height for Russian swings unless you have advanced stability for American swings.
-
Controlled Movement: Don’t let the kettlebell pull you down—control both the ascent and descent.
-
Start Light: Practice form with a lighter kettlebell before progressing to heavier weights.
Benefits
-
Builds explosive power through hips and glutes.
-
Strengthens posterior chain: hamstrings, glutes, and lower back.
-
Improves cardiovascular conditioning and endurance.
-
Enhances grip strength and forearm endurance.
-
Boosts core stability and posture.
-
Burns calories quickly for fat loss and conditioning.
The kettlebell swing is a powerful, full-body exercise that delivers both strength and conditioning benefits. By focusing on proper hip hinge mechanics, core stability, and controlled movement, you can safely perform swings to build muscle, increase power, and improve athletic performance. Start light, perfect your form, and progress gradually for maximum results.